Table of Contents
Introduction
The goal of this project is to explore model selection procedures using cross-validation on selecting polynomial degree of feature for a model. Following this, additional testing was done on reducing over-fitting by demeaning the data and introducing a regularization parameter.
Polynomial degree model selection
The first model took a provided dataset with 31 observations, one target variable and one feature, and split it randomly in 19 training observations, 6 cross validation observations and 6 testing observations.
The necessity for cross validation is shown clearly in the below cost figure. for the training set, the addition of new features will almost always be a decrease in cost and hence and improvement to the model. However, this is not necessarily the case for the cross-validation set under the same model, as the model could suffer from over-fitting at higher order polynomials.
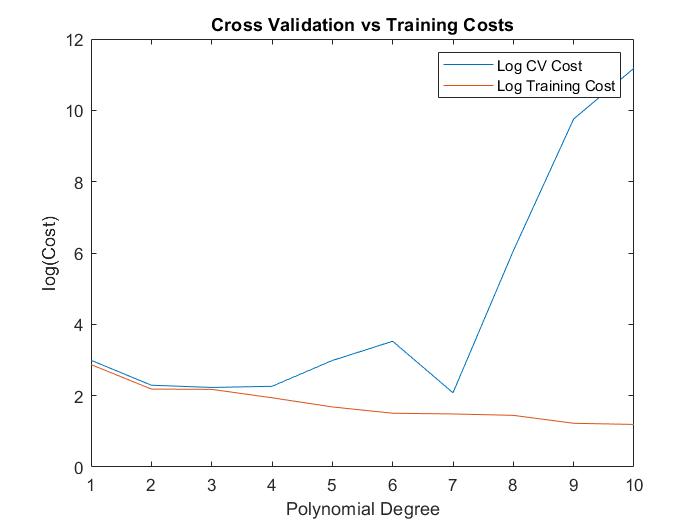
The cross validation process suggests that polynomial degree 7 for this specific rng seed would be the best model. Following this, the degree 7 model was tested using the test set, providing a final cost of 94.2488.
Regularization
In order to reduct the impact of over-fitting on the model, a test was conducted to implement an optimal regularization parameter into the model. First, the data from the data set was demeaned. We then assumed a model that had polynomial degree of 10 for the feature. Following this, the model was iterated with regularization parameter between 0 to 1 in increments of 0.001 on the training set. The models were then validated using the cross validation set, to derive a final optimal regularization parameter of 0.1.
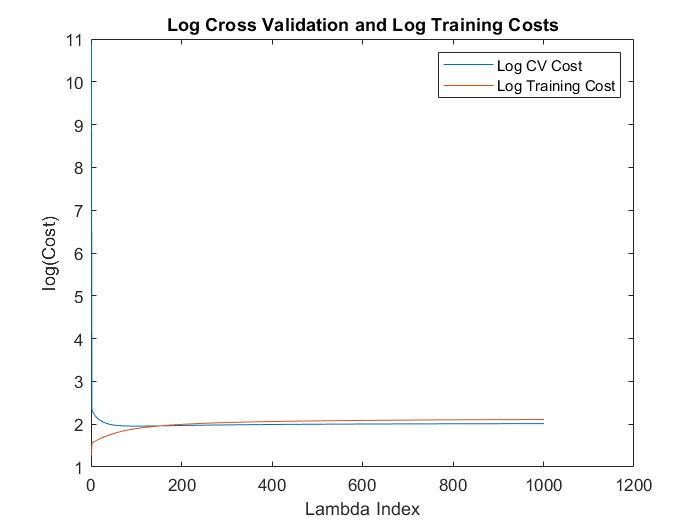
As shown in the above figure, the models experience a sharp drop in cost up to the optimal regularization parameter, with the cost then increasing to a constant as the regularization parameter rises past the optimum. This convergence to constancy is due to the penalty term outweighing the importance of the cost minimization in the minimization function, resulting in the model selecting theta coefficients with value 0 in order to avoid suffering from penalty.
The test set cost using lambda = 0.1 was 7.0659.
Code
The full self written MATLAB code and dataset used is available on the github page for the project.
Take Aways
-
Cross validation is very important in model selection, since it allows us to check for factors such as over-fitting in the model, and prevents randomness from overly influencing our final model choice. Without cross validation, it is possible that our model overfits to the randomly generated training and test models, and performs extremely poorly in a predictive setting with out of sample observations.
-
Regularization is a strong tool in reducing the impact of overfitting in a model. It is important to note that the regularization parameter could be an extremely small number. Increases over optimum could result in the model converging to a constant cost due to the severity of the penalty term in the model.
